Who was behind WannaCry ransomware?
The Lazarus Group is widely believed to have been behind several headline-grabbing hacks, including the breach of Sony Pictures in 2014 and the WannaCry ransomware hack in 2017, which affected hundreds of thousands of computers in 150 countries.
Is WannaCry still active in 2021?
While the majority of the damage occurred in the weeks after , WannaCry ransomware attacks actually increased 53% from January 2021 to March 2021. While researching my in-depth article WannaCry: How the Widespread Ransomware Changed Cybersecurity, I learned that WannaCry attacks are still found today.
How does WannaCry ransomware work?
WannaCry ransomware is a crypto ransomware worm that attacks Windows PCs. It’s a form of malware that can spread from PC to PC across networks (hence the « worm » component) and then once on a computer it can encrypt critical files (the « crypto » part). The perpetrators then demand ransom payments to unlock those files.
Is WannaCry still a threat 2020?
It’s true that WannaCry is no longer trending. New (or recycled) malware strains, such as Maze, Netwalker, RagnarLocker or Ryuk (not to mention the recently fallen Emotet), appear far more active and threatening.
Was North Korea behind WannaCry?
The US and UK governments have said North Korea was responsible for the WannaCry malware attack affecting hospitals, businesses and banks across the world earlier this year. The attack is said to have hit more than 300,000 computers in 150 nations, causing billions of dollars of damage.
How was the WannaCry ransomware stopped?
The attack began at 07:44 UTC on and was halted a few hours later at 15:03 UTC by the registration of a kill switch discovered by Marcus Hutchins. The kill switch prevented already infected computers from being encrypted or further spreading WannaCry.
What is eternal blue exploit?
EternalBlue exploits SMBv1 vulnerabilities to insert malicious data packets and spread malware over the network. The exploit makes use of the way Microsoft Windows handles, or rather mishandles, specially crafted packets from malicious attackers.
What is the most popular ransomware in history?
WannaCry
1. WannaCry. In May 2017, Companies across the world were attacked by a fast-spreading piece of malware known as WannaCry. This ransomware infected 7000 computers in the first hour and 110000 distinct IP addresses in two days, making WannaCry one of the most notoriously destructive ransomware attacks of all time.
Was WannaCry a Trojan?
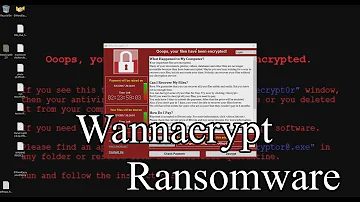
Description. WannaCry is a ransomware cryptoworm, which targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system by encrypting (locking) data and demanding ransom payments in the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. The worm is also known as WannaCrypt, Wana Decrypt0r 2.0, WanaCrypt0r 2.0, and Wanna Decryptor.
How much money did WannaCry make?
As the ransomware spread beyond Europe, computer systems in 150 countries were crippled. The WannaCry ransomware attack had a substantial financial impact worldwide. It is estimated this cybercrime caused $4 billion in losses across the globe.
How to protect from WannaCry?
- The most effective way to protect yourself from WannaCry – or any other type of ransomware – is to prepare ahead of time. Once your system is infected, there’s no realistic way to decrypt all of your data without paying the ransom – and even that’s no guarantee.
What is WannaCry or Wanna Decryptor ransomware on Earth?
- WannaCry is a ransomware cryptoworm , which targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system by encrypting data and demanding ransom payments in the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. The worm is also known as WannaCrypt, Wana Decrypt0r 2.0, WanaCrypt0r 2.0, and Wanna Decryptor.
Is WannaCry still active?
- WannaCry is still active on the Internet, as is Petya and countless other exploits.
What does Wanna Cry malware?
- WannaCry which is sometimes also called WCry or WanaCryptor is a ransomware malware, meaning that it encrypts files of its victims and demands a payment to restore the stolen information, usually in bitcoin with ransom amounts ranging from $300 to $600 equivalents.
